AI-powered Operational Efficiency Analysis for Informed Business Optimization
Problem
The Data Complexities in Traditional Operational Efficiency Analysis
Operational efficiency is a critical factor in the finance and banking industry. Maintaining efficient operations is a constant challenge with the ever-increasing complexity of financial transactions, regulatory requirements, and customer demands. Traditional processes are often manual, time-consuming, and error-prone, posing challenges amidst the complex nature of financial data and the vast amount of information available. ZBrain offers a solution for enhancing operational efficiency and maximizing success.
Solution
I. How ZBrain Flow Enhances Operational Efficiency Analysis
ZBrain Flow automates and accelerates manual operational efficiency analysis processes by leveraging AI and ML capabilities. Below is a comparative breakdown of the time and effort required for each analysis task with and without ZBrain Flow:
| Steps | Without ZBrain Flow | Time Without ZBrain Flow | With ZBrain Flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Collection and Aggregation | Manual | ~6 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Data Cleaning and Preprocessing | Manual | ~6 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Data Analysis and Modeling | Manual | ~10 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Report Generation | Manual | ~6 hours | Automated by ZBrain Flow |
| Report Review and Finalization | Manual | ~2 hours | Manual |
| Total | ~30 hours | ~4 hours |
II. Necessary Input Data
For ZBrain to operate effectively and produce accurate financial analysis reports, it requires the following data sources:
| Information Source | Description | Recency |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Statements | Company financial reports, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements | Last fiscal quarter |
| Market Data | Real-time and historical market data, including stock prices, interest rates, and economic indicators | Always updated |
| Credit Reports | Credit ratings, credit history, and financial health information for companies and individuals | Last fiscal year |
| Regulatory Filings | Publicly available regulatory filings, including 10-K, 10-Q, and annual reports | Last fiscal year |
| Transaction Data | Data on financial transactions, investments, and trades | Real-time |
III. ZBrain Flow: How It Works?
Step 1: Data Gathering and Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
In the first stage of operational efficiency analysis, ZBrain begins by collecting relevant data, which includes financial statements, operational metrics, customer transaction data, regulatory records, and market indicators from various sources. Once the data is acquired, ZBrain performs automated EDA, validating and cleaning it to ensure its accuracy and consistency. This crucial step is vital for preventing analytical errors and maintaining the integrity of operational insights.
Step 2: Embedding Generation
ZBrain transforms textual data into numerical representations using advanced embedding techniques during this phase. These embeddings capture contextual relationships between data points, enhancing the efficiency of retrieval and analysis. ZBrain utilizes this capability to provide accurate insights, enhancing the decision-making process for improved operational efficiency.
Step 3: Query Execution and Report Generation
When a user requests an operational efficiency analysis report, ZBrain extracts the pertinent data based on the query’s criteria. This data, coupled with the user’s inquiry, undergoes processing by the OpenAI Language Model (LLM) to produce a comprehensive report.
Leveraging the acquired data, the LLM generates a well-structured report encompassing operational insights, efficiency recommendations, and facilitating understanding for decision-makers.
Step 4: Parsing the Generated Report
Following report generation, ZBrain employs a parsing technique to refine the report, extracting only the most relevant insights. Any necessary improvements are implemented to ensure the report’s highest quality and ability to guide operational decision-making effectively.
ZBrain integrates data collection, validation, analysis, parsing and report creation to produce a holistic operational efficiency analysis report, empowering professionals in the finance and banking sector with valuable insights for formulating well-informed operational strategies.
Result
Enhanced Operational Efficiency in Financial Analysis
ZBrain substantially improves operational efficiency in finance and banking by equipping financial professionals with data-driven decision-making capabilities for critical operational tasks. The traditional manual approach, which took approximately 30 hours, is streamlined to around 4 hours, resulting in remarkable time and cost savings. With ZBrain, finance and banking professionals can make data-driven decisions swiftly, reduce operational costs, and optimize customer interactions. Embrace ZBrain Flow to unlock unparalleled operational efficiency and enhance the organization’s success.
Example Report
Prompt:
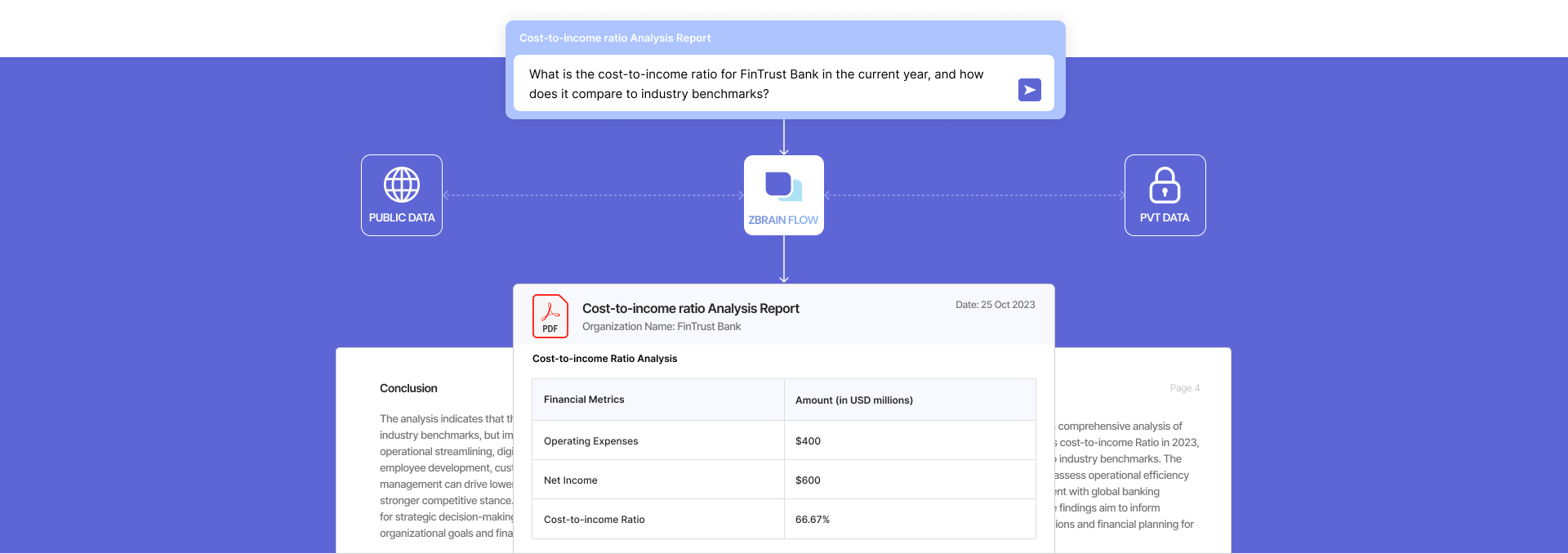
What is the cost-to-income ratio for FinTrust Bank in the current year, and how does it compare to industry benchmarks?
Executive Summary
This report is a comprehensive analysis of FinTrust Bank’s cost-to-income Ratio in 2023, comparing it to industry benchmarks. The objective is to assess operational efficiency and its alignment with global banking standards. The findings aim to inform strategic decisions and financial planning for the bank.
Methodology
- Data Collection:
-
Gathered FinTrust Bank’s financial data for the year 2023, specifically focusing on operating expenses and net income.
-
Ensured accuracy and reliability of the data by cross-referencing with official financial statements and reports.
- Cost-to-income Ratio Calculation:
-
Calculated the cost-to-income ratio by dividing the total operating expenses by the net income and expressing the result as a percentage.
-
Formula: Cost-to-income Ratio = (Operating Expenses / Net Income) * 100.
- Industry Benchmark Research:
-
Researched industry benchmarks for the cost-to-income ratio in various banking segments, including global banking organizations, regional banks, savings and loan associations, and online-only banks. Identified benchmark ranges for each segment based on industry reports, financial publications, and credible banking sources.
- Benchmark Comparison:
-
Compared FinTrust Bank’s cost-to-income ratio with the identified industry benchmark ranges to assess its performance relative to global standards.
- Analysis and Interpretation:
-
Interpreted the findings to evaluate the operational efficiency of FinTrust Bank.
-
Analyzed the implications of the cost-to-income ratio within the context of industry benchmarks to provide a comprehensive understanding of the bank’s performance.
Cost-to-income Ratio Analysis
| Financial Metrics | Amount (in USD millions) |
|---|---|
| Operating Expenses | $400 |
| Net Income | $600 |
| Cost-to-Income Ratio | 66.67% |
The cost-to-income ratio for FinTrust Bank in 2023 is 66.67%, indicating that the bank allocates approximately 66.67 cents to operational expenses for every dollar of income.
Industry Benchmark Comparison
| Industry Segment | Cost-to-Income Ratio Range |
|---|---|
| Global Banking Organizations | 60% – 70% |
| Regional Banks | 70% – 80% |
| Savings and Loan Associations | 75% – 85% |
| Online-Only Banks | 50% – 60% |
Based on the industry benchmark ranges, it can be concluded that:
-
FinTrust Bank’s cost-to-income ratio (66.67%) falls within the range for “Global banking organizations” (60% – 70%). This suggests that FinTrust Bank is operating within the expected efficiency parameters for a bank of its scale globally.
-
However, it’s important to note that while the ratio is within the acceptable range, there may still be opportunities to improve operational efficiency to move closer to the lower end of the range, thus enhancing profitability.
Recommendations
To enhance operational efficiency and potentially reduce the cost-to-income ratio, FinTrust Bank can consider the following strategies:
-
Streamlining operational processes: Continuously review and optimize operational processes to identify cost-saving opportunities.
-
Digital transformation: Invest in digital technologies and automation to reduce manual processes and associated costs.
-
Cost control measures: Implement strict measures to monitor and manage operational expenses effectively.
-
Employee training and development: Ensure employees are well-trained and equipped to perform their roles efficiently, leading to lower operational costs.
-
Customer segmentation: Identify and focus on high-value customer segments to increase revenue while controlling costs.
-
Risk management: Implement robust risk management practices to mitigate potential losses that could impact the cost structure.
Conclusion
The analysis indicates that the cost-to-income ratio aligns with industry benchmarks, but improvements are possible. Prioritizing operational streamlining, digital transformation, cost control, employee development, customer segmentation, and risk management can drive lower ratios, heightened profitability, and a stronger competitive stance. This analysis serves as a foundation for strategic decision-making, aligning budgets with organizational goals and financial targets.


