Intranet search engine guide: How it works, use cases, challenges, and solutions

Listen to the article
Efficient access to information within an organization is no longer a nice-to-have capability—it is a business necessity. In today’s digital-first workplaces, employees rely on internal systems to access policies, project documentation, training materials, and operational knowledge required to perform their roles effectively. Yet as enterprise content continues to grow and spread across intranets, collaboration tools, and document repositories, many organizations struggle to ensure that critical information is easy to find, reliable, and up to date.
The cost of ineffective internal search is high and measurable. An enterprise employing 1,000 knowledge workers can waste approximately $48,000 per week, nearly $2.5 million annually, simply due to employees’ inability to locate and retrieve information efficiently. This loss stems from duplicated work, delayed decisions, and repeated requests for the same knowledge across teams.
These challenges are reflected in the growing strategic importance of workplace search technologies. The global enterprise search market was valued at USD 5.34 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 12.71 billion by 2035, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.05%. This sustained growth underscores how organizations are increasingly prioritizing search and information discovery as foundational elements of their digital workplace strategies.
Within this evolving landscape, intranet search engines play a pivotal role. Far more than a basic keyword function, a modern intranet search engine enables employees to quickly surface relevant, accurate, and permission-aware information from internal portals and knowledge hubs. When implemented effectively, it reduces friction, supports faster decision-making, and transforms the intranet into a true system of engagement.
This guide explores what intranet search engines are, how they work, key enterprise use cases, common challenges that limit their effectiveness, and best practices for building scalable search experiences for modern digital workplaces. It also examines how enterprise search solution such as ZSearch extend these capabilities beyond the intranet—enabling secure, AI-powered discovery across the broader enterprise knowledge ecosystem.
- What is an intranet search engine, and why does it matter?
- Intranet search vs. web search: Key differences in enterprise environments
- The anatomy of a modern intranet search engine
- Enterprise use cases for intranet search
- Key challenges limiting the effectiveness of intranet search
- Benefits of intranet search engines
- ZSearch: Expanding enterprise knowledge discovery beyond traditional intranet search
What is an intranet search engine, and why does it matter?
An intranet search engine is a specialized tool designed to help employees quickly and accurately locate information within an organization’s internal systems and data sources. It enables search across intranet pages, documents, policies, files, and other internal resources from a single interface, ensuring that relevant information can be accessed without navigating complex menus or folder structures. Built specifically for enterprise use, intranet search engines account for organizational context, content structure, and access permissions to deliver precise and secure results.
At a deeper level, an intranet search engine functions as a discovery layer for an organization’s private digital ecosystem. Rather than forcing employees to remember where information resides—whether in a document repository, a collaboration platform, or a legacy system—it provides a single, consistent point of entry to internal knowledge. By enforcing permission-aware access (often referred to as security trimming), the search engine ensures that users only see information they are authorized to access, preserving privacy and compliance.
Why intranet search matters
As digital workplaces continue to expand, internal information is no longer confined to a single system. Content is increasingly distributed across intranets, document repositories, collaboration tools, and line-of-business applications. Without effective search capabilities, employees are forced to rely on manual browsing or repeated requests to colleagues, leading to inefficiencies, duplicated work, and frustration.
An effective intranet search engine helps address these challenges by centralizing discovery within the intranet and making internal knowledge easier to find and use. It reduces time spent searching, preserves institutional knowledge as teams change, and minimizes the digital friction that erodes trust in internal systems. When information is consistently discoverable, employees are better equipped to make decisions, collaborate effectively, and stay aligned with organizational processes.
From keywords to intent
Modern intranet search engines go beyond simple keyword-based retrieval. They leverage semantic understanding, metadata, and intelligent ranking to interpret user intent and surface the most relevant information in context. Instead of returning long lists of loosely related results, these systems prioritize accuracy, relevance, and usability—helping employees reach the right information faster.
In essence, an intranet search engine serves as the foundation for effective information access within an organization. When combined with strong content governance and intranet best practices, it transforms the intranet from a static repository into a reliable, intelligent knowledge hub that supports collaboration, communication, and efficient day-to-day operations.
Intranet search vs. web search: Key differences in enterprise environments
Although search may appear to be a universal problem, searching within an organization is fundamentally different from searching the public web. The two environments operate under distinct constraints, expectations, and risks—making intranet search a unique challenge.
Security and permissions are non-negotiable
One of the most critical distinctions between intranet and web search is security. Public search engines are designed to maximize visibility, whereas intranet search must strictly enforce access controls. Search results must respect roles, departments, and compliance requirements at all times.
This requirement—often referred to as security trimming—ensures employees only see content they are authorized to access. Unlike web search, enterprise search must never “over-share.” Even a single permissions failure can expose sensitive information and undermine trust in internal systems.
Why ranking works differently inside organizations
Web search engines rely on popularity signals such as links, click behavior, and engagement metrics to determine relevance. Algorithms such as PageRank use backlinks and collective behavior to identify authoritative content. Employees rarely link to internal policies or procedural documents.
As a result, intranet search engines must rely on enterprise-specific signals—such as metadata quality, document status, ownership, and recency—to rank results effectively. Poor metadata directly leads to poor search results, making content governance and taxonomy essential components of intranet search success.
The challenge of enterprise language
Enterprises also introduce language complexity. Every organization develops its own acronyms, project names, and internal terminology. A search engine must understand that different terms may refer to the same concept, even if the language used by employees does not match the wording in official documents.
To address this, intranet search engines depend on synonym management and taxonomies that map informal queries to structured content, ensuring relevant information is discoverable regardless of how employees phrase their searches.
Intent-driven search at work
Finally, user intent in the workplace is task-focused rather than exploratory. Employees search to complete actions—such as locating a policy, accessing a system, or understanding a process. Intranet search must recognize this intent and surface the most relevant, authoritative information quickly, rather than overwhelming users with volume.
These differences explain why intranet search requires a purpose-built approach—and why applying web search assumptions inside the enterprise often falls short.
Streamline your operational workflows with ZBrain AI agents designed to address enterprise challenges.
The anatomy of a modern intranet search engine
A modern intranet search engine is more than a simple keyword-matching tool. It is a layered system designed to discover, organize, and deliver information from across an organization’s internal environment in a way that is fast, secure, and context-aware. While implementations may vary, most intranet search engines rely on a common set of foundational components.
Indexing and connectors: Discovering internal content
At the foundation of intranet search is the ability to discover and index content from multiple internal sources. Search engines use connectors, APIs, and crawlers to scan systems such as intranet portals, document repositories, collaboration tools, and business applications. These may include platforms like SharePoint, Google Drive, Jira, Confluence, or internal knowledge bases.
During this process, the search engine collects both full-text content and metadata—such as titles, authors, dates, departments, and permissions—and stores it in a searchable index. This indexed layer acts as a structured map of the organization’s knowledge, enabling fast retrieval without querying each system individually at search time.
Federated search: One experience, many systems
In many organizations, information is spread across disconnected platforms. Federated search addresses this challenge by enabling employees to search once and retrieve results from multiple systems through a single interface. Rather than forcing users to know where information lives, federated search abstracts system boundaries and presents a unified discovery experience.
This approach reduces tool-switching, improves findability, and ensures that employees can access relevant information regardless of its source—provided they have permission to view it.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Understanding intent
Traditional keyword search relies on exact term matching, which often fails in real-world workplace scenarios. Modern intranet search engines increasingly use Natural Language Processing (NLP) to interpret intent, understand synonyms, and handle conversational queries.
For example, a query phrased as a question can be mapped to relevant policies, guides, or resources even if its wording does not exactly match a document title. NLP allows search systems to move from literal matching to intent-based discovery, making search more intuitive and effective for employees.
Ranking and relevance: Deciding what comes first
Once results are retrieved, the search engine must determine which ones are most useful. Unlike web search, intranet search cannot rely solely on popularity signals. Instead, it balances multiple relevance factors, including:
- Recency, to reflect updated information
- Authority, such as official or approved documents
- Contextual factors, such as user role or department
The goal is to surface the most accurate and appropriate information, not simply the newest or most frequently accessed content.
Faceted search and filters: Reducing cognitive load
To help users refine results quickly, modern intranet search engines provide filters and facets—such as department, date, file type, or content source. These tools reduce cognitive load by allowing employees to narrow large result sets without having to rephrase queries repeatedly.
Combined with features like autocomplete and suggestions, filters help employees reach the right information faster and with less effort.
Together, these components form the technical backbone of a modern intranet search engine—enabling efficient discovery, secure access, and a more intuitive way to navigate an organization’s growing body of knowledge.
As organizations mature digitally, many find that even the most advanced intranet search capabilities are only part of the solution. While intranet search engines are designed to optimize discovery within internal portals and curated knowledge hubs, modern workplaces often require search to extend beyond these to a broader ecosystem of enterprise tools and systems.
This is where enterprise search solutions such as ZSearch come into play. Built to go beyond traditional intranet boundaries, ZSearch applies the same principles of secure indexing, intent-aware search, and relevance ranking across a wider range of enterprise data sources. By unifying discovery across documents, collaboration tools, and business systems, it represents the next step in the evolution of workplace search—one that complements intranet search while addressing the complexity of enterprise-wide knowledge environments.
Enterprise use cases for intranet search
An intranet search engine supports far more than basic document retrieval. When implemented effectively, it becomes a core productivity layer—enabling employees to find information, complete tasks, and make decisions faster across a wide range of everyday scenarios. Below are key enterprise use cases that highlight the practical value of intranet search.
1. Quickly finding updated company policies
Company policies are among the most frequently accessed—and most time-sensitive—internal documents. Employees regularly search for answers to questions such as:
- What is the current dress code?
- When is the next company holiday?
- What steps should I follow for an unplanned leave of absence?
Intranet search provides on-demand access to the most current, authoritative policies, reducing dependency on HR and minimizing the risk of outdated guidance. This is especially valuable in sensitive situations where employees prefer to find information privately and quickly.
2. Accessing relevant team resources
Intranet search enables access to shared folders, project files, and reference materials that employees are authorized to view, ensuring teams work with the latest versions. Instead of navigating complex folder structures or requesting files from colleagues, employees can search directly and see when content was last updated and by whom.
This improves collaboration, reduces version confusion, and ensures consistency across teams.
3. Finding individual employee details
Advanced intranet search makes employee directories more useful by enabling the discovery of:
- Employee locations or time zones
- Skills, expertise, and certifications
- Birthdays and work anniversaries
Managers and HR teams can use this information to improve workforce planning, strengthen recognition programs, and assign work based on skills rather than guesswork.
4. Enabling IT self-service
Employees can resolve common technical issues independently by using the intranet search to find:
- Troubleshooting guides
- System documentation
- How-to videos
- Open or resolved ticket references
By reducing reliance on helpdesk tickets for routine issues, intranet search frees IT teams to focus on higher-impact initiatives.
5. Supporting new employee onboarding
For new hires, intranet search serves as a critical onboarding companion. It provides easy access to training materials, policies, role-specific documentation, and internal processes—allowing employees to ramp up faster and with greater confidence.
A strong search experience during onboarding sets the tone for long-term engagement and self-sufficiency.
6. Fostering knowledge base adoption
A centralized knowledge base is only effective if employees can easily find and use it. Intranet search ensures that FAQs, how-to articles, and shared expertise are surfaced at the moment of need.
As usage increases, search systems can learn from employee behavior to improve relevance—creating a continuous improvement loop between content and discovery.
7. Supporting compliance and audit readiness
In regulated industries, employees often need fast access to approved procedures, compliance guidelines, and audit documentation. Intranet search helps teams locate:
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- Compliance checklists
- Approved templates and records
This reduces risk, improves consistency, and ensures employees follow the most up-to-date guidance.
8. Improving internal communications and announcements
Important updates—such as leadership messages, organizational changes, or operational announcements—can quickly become buried in feeds or email threads. Intranet search ensures employees can retrieve past communications when they need context or clarification.
This is particularly valuable for distributed teams and employees working across time zones.
9. Enabling cross-department collaboration
Intranet search helps break down silos by making knowledge discoverable across departments. Employees can find:
- Best practices from other teams
- Shared templates and playbooks
- Subject-matter experts across the organization
This encourages reuse of existing knowledge, reduces duplicated effort, and promotes a more connected workplace.
Across all these scenarios, intranet search delivers the same core benefits: faster access to information, reduced friction, and greater employee autonomy. When employees can reliably find what they need, organizations operate more efficiently—and internal knowledge becomes a strategic asset rather than a hidden cost.
Key challenges limiting the effectiveness of intranet search
While intranet search engines are critical to enabling efficient information access, they rarely work optimally out of the box. As organizations grow and content volumes increase, several common challenges can undermine search accuracy, usability, and adoption. Addressing these challenges requires a combination of technology, governance, and ongoing optimization.
1. Incomplete indexing and data silos
One of the most common issues with intranet search is incomplete or outdated indexing. Beyond technical misconfiguration, this problem is often amplified by data silos—where information is spread across disconnected systems such as intranets, document repositories, collaboration tools, and ticketing platforms. When content is not indexed uniformly, employees risk working with inaccurate or incomplete information.
How to overcome it:
Modern intranet search engines use a combination of scheduled crawlers, event-based indexing, and content connectors to continuously monitor changes across systems. AI-driven indexing can further help by detecting updates in real time, flagging stale content, and ensuring that authoritative sources remain searchable regardless of where they reside.
2. Poor search relevance and accuracy
Employees frequently encounter search results that feel generic or noisy, even when relevant content exists. Traditional intranet search engines relied primarily on lexical search techniques, leading to results that match keywords but not meaning.
How to overcome it:
Modern intranet search engines use semantic and vector-based search techniques to interpret intent rather than relying solely on keyword frequency. Relevance can be further improved through rank tuning, where enterprise-specific signals—such as document type, approval status, or folder authority—are deliberately weighted so that official policies consistently outrank drafts or informal files.
3. Inconsistent tagging and metadata
Inconsistent naming conventions and poorly managed metadata significantly reduce search effectiveness. When teams apply different labels to similar content—or skip tagging altogether—search engines lose critical context needed for accurate retrieval.
How to overcome it:
Establishing a standardized taxonomy and metadata framework is essential. Advanced search systems can also compensate for inconsistencies by supporting synonym libraries, flexible schema indexing, and metadata enrichment—helping normalize content without requiring perfect human input.
4. Information overload and disorganized results
As intranets grow, employees may be overwhelmed by the sheer volume of content returned by a single query. Poorly structured results increase cognitive load and make it harder to identify the most useful information quickly.
How to overcome it:
Faceted navigation, intelligent filters, and relevance-based ranking help users narrow results efficiently. Increasingly, organizations are also adopting AI-powered answer generation, where search engines summarize key information from multiple documents using Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), reducing the need to open and compare several files manually.
5. Security and access control conflicts
Search engines must strike a careful balance between accessibility and security. Misconfigured permissions can either expose sensitive data or overly restrict access, both of which erode trust.
How to overcome it:
Effective intranet search engines enforce permission-aware indexing—commonly known as security trimming—ensuring that results are filtered at query time based on the user’s current access rights. Audit trails and content classification further strengthen governance and compliance.
6. Low user adoption and search literacy
Even technically sound search systems can fail if employees do not trust or understand how to use them effectively. Lack of familiarity with filters or advanced features often leads to underutilization.
How to overcome it:
An intuitive search interface with autocomplete, predictive suggestions, and minimal learning curves encourages adoption. Search analytics—such as tracking zero-result queries or low click-through rates—enable continuous optimization of both content and ranking logic.
These challenges highlight an important reality: intranet search is not a static feature, but an evolving capability. Its success depends on continuous tuning across data sources, relevance signals, security, and user behavior. Organizations that actively manage these elements are far more likely to deliver a trusted, efficient search experience—transforming their intranet from a content repository into a true knowledge enablement platform.
Streamline your operational workflows with ZBrain AI agents designed to address enterprise challenges.
Benefits of intranet search engines
An effective intranet search engine delivers tangible benefits across productivity, collaboration, and knowledge accessibility. When search is treated as a core capability rather than a basic feature, it becomes a powerful enabler of modern digital work.
Centralized access to information
Intranet search provides a single point of access to internal policies, announcements, onboarding materials, and operational documents. Employees no longer need to navigate multiple portals or folder structures, reducing friction and improving day-to-day efficiency.
Improved organization and findability
By automatically indexing and structuring content using metadata and tags, intranet search engines ensure information remains discoverable as content volumes grow. This significantly reduces time spent searching and increases confidence in internal systems.
Faster, more informed decision-making
Quick access to relevant and up-to-date information enables employees to make decisions faster. Instead of waiting for colleagues’ responses or revalidating documents, teams can act with clarity and confidence.
Enhanced data security and compliance
Modern intranet search engines enforce role-based access controls and permission-aware indexing. Employees only see information they are authorized to access, ensuring sensitive data remains protected while maintaining transparency.
Greater employee engagement and collaboration
Easy discovery of people, resources, and internal communications improves collaboration across teams. Employees are empowered to work independently while staying connected to organizational knowledge and expertise.
Reduced IT and support burden
By enabling self-service access to documentation, guides, and troubleshooting resources, intranet search reduces the need for routine support requests. IT teams can focus on strategic initiatives instead of repetitive queries.
Stronger knowledge management
Intranet search supports better knowledge capture, reuse, and sharing across the organization. As employees rely more on search, the knowledge base becomes increasingly valuable and continues to improve.
AI-powered enhancements
AI-driven intranet search further improves relevance and usability through semantic understanding and intent-based retrieval. By learning from user behavior and search patterns, AI helps surface more accurate results over time, increasing productivity and improving the overall employee experience.
ZSearch: Expanding enterprise knowledge discovery beyond traditional intranet search
Modern digital workplaces require search capabilities that extend beyond individual portals and content silos. While intranet search plays a vital role in organizing internal information, enterprise-scale discovery increasingly demands a unified, AI-driven approach. ZSearch is designed to meet this need by enabling secure, context-aware search across the broader enterprise knowledge ecosystem.
ZSearch is an AI-powered enterprise search solution that enables unified, permission-aware discovery across an organization’s entire knowledge ecosystem. It integrates with internal systems to index documents, messages, tickets, and local files, etc. allowing employees to access information through both keyword-based and natural language queries—without needing to know where that information lives.
Secure, seamless connectivity
ZSearch securely integrates with platforms such as Google Drive, SharePoint, Slack, GitHub, and Jira, enabling enterprise knowledge search through a single portal. Permissions are enforced end-to-end, ensuring users only see content they are authorized to access. This allows organizations to unify search across systems while maintaining strict security and governance.
Contextual search results
ZSearch interprets natural language queries and user intent to deliver contextually relevant results grounded in an organization’s unique knowledge environment. Its semantic understanding improves relevance by matching meaning rather than relying solely on keywords, reducing noise and improving accuracy across diverse content sources.
Collaborative workspace
ZSearch turns search into a collaborative workflow. Users can group multiple search results into shared project workspaces, each supported by a dedicated AI assistant. These workspaces help teams organize findings, explore related content, and act on information together without switching tools.
Natural language search and retrieval
ZSearch enables natural language search and retrieval through unified search, providing a single, centralized portal across enterprise data sources. Its hybrid retrieval model combines keyword-based and semantic search, while smart ranking prioritizes results using contextual relevance. Targeted content discovery further refines results by data source, content type, and recency, reducing time-to-find.
Semantic understanding
Semantic understanding ensures context-aware results, enabling the search engine to interpret intent and meaning rather than relying solely on keywords. This allows users to retrieve more relevant information even when terminology varies across teams or systems.
Personalized and collaboration-ready
ZSearch supports project creation by allowing users to group search results into focused workspaces. Each project includes an AI assistant that answers questions using project-specific content, enabling shared exploration and collaborative decision-making across teams.
Secure and permission-aware
Built with enterprise-grade security, ZSearch enforces identity-based access control at every layer. Controlled data access ensures zero data leakage, while source traceability maintains transparency into the origin of information. The platform is compliance-ready and aligns with a range of standards.
How ZSearch goes beyond intranet search
While intranet search engines optimize discovery within internal portals, ZSearch extends search across the full enterprise knowledge landscape. By combining unified search, hybrid retrieval, semantic understanding, collaboration-ready workflows, and enterprise-grade security, ZSearch complements intranet search and addresses the complexity of modern, distributed information environments.
Endnote
Effective intranet search is a cornerstone of the modern digital workplace, enabling employees to find trusted information quickly and work with greater confidence. As content volumes grow and knowledge spreads across multiple systems, organizations must move beyond basic keyword search to deliver experiences that are accurate, secure, and intent-aware.
While intranet search addresses discovery within internal portals, today’s enterprises increasingly require broader, AI-powered search capabilities that unify access across tools and platforms. By building on strong intranet search foundations and extending them with enterprise search solutions like ZSearch, organizations can reduce friction, improve decision-making, and make internal knowledge truly accessible.
Ultimately, the success of any search strategy lies in its ability to deliver the right information at the right time—securely, contextually, and without friction. Organizations that treat search as a strategic capability are better positioned to unlock the full value of their collective knowledge and keep pace with an evolving workplace.
Intranet search is essential, but modern workplaces demand more—discover how ZSearch extends search across the enterprise with AI. Book a demo.
Listen to the article
Author’s Bio

An early adopter of emerging technologies, Akash leads innovation in AI, driving transformative solutions that enhance business operations. With his entrepreneurial spirit, technical acumen and passion for AI, Akash continues to explore new horizons, empowering businesses with solutions that enable seamless automation, intelligent decision-making, and next-generation digital experiences.
Table of content
- What is an intranet search engine, and why does it matter?
- Intranet search vs. web search: Key differences in enterprise environments
- The anatomy of a modern intranet search engine
- Enterprise use cases for intranet search
- Key challenges limiting the effectiveness of intranet search
- Benefits of intranet search engines
- ZSearch: Expanding enterprise knowledge discovery beyond traditional intranet search
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an intranet search engine?
Beyond basic retrieval, a well-designed intranet search engine supports productivity by reducing navigation effort, minimizing duplicate work, and ensuring employees rely on approved and up-to-date information. It plays a foundational role in enabling efficient knowledge sharing within the intranet.
How is intranet search different from web search?
Additionally, intranet search must understand organizational structure, internal terminology, and compliance requirements—factors that are irrelevant in public web search but critical inside enterprises.
How does AI improve intranet search?
AI can reduce noise in results, improve accuracy for complex queries, and help employees reach answers faster—especially when information is scattered or phrased inconsistently.
What is ZSearch?
What are the key capabilities of ZSearch?
- Unified search: Enables a single, centralized search experience across enterprise systems and data sources.
- Hybrid retrieval: Combines keyword-based and semantic search to deliver contextually relevant results.
- Smart ranking: Prioritizes results using relevance signals and contextual understanding to surface authoritative content.
- Semantic understanding: Interprets user intent to provide context-aware search results rather than exact keyword matches.
- Collaborative workspaces: Allows users to group search results into projects and access project-level AI assistants.
- Enterprise-grade security: Enforces permission-aware access with full security trimming and controlled data visibility.
- Source traceability: Maintains transparency by clearly indicating the origin of search results.
What are the key benefits of using ZSearch for enterprises?
How does ZSearch ensure secure and permission-aware enterprise search?
ZSearch enforces enterprise-grade security by respecting source-level permissions and Access Control Lists (ACLs) across all connected systems. Users can access only the information they are authorized to view, with permissions enforced end-to-end throughout the search and retrieval process. ZSearch is designed to align with major compliance frameworks, ensuring secure and compliant knowledge discovery across the organization.
How can organizations get started with ZSearch?
Organizations can get started with ZSearch by visiting our solution and booking a demo. During the demo, teams can explore how ZSearch connects to existing enterprise systems, enables secure and intelligent search across data sources, and supports collaboration using permission-aware access. The onboarding process is designed to integrate seamlessly with existing workflows, enabling organizations to quickly realize value without disrupting operations.
Insights
Enterprise knowledge management guide
Enterprise knowledge management enables organizations to capture, organize, and activate knowledge across systems, teams, and workflows—ensuring the right information reaches the right people at the right time.

Company knowledge base: Why it matters and how it is evolving
A centralized company knowledge base is no longer a “nice-to-have” – it’s essential infrastructure. A knowledge base serves as a single source of truth: a unified repository where documentation, FAQs, manuals, project notes, institutional knowledge, and expert insights can reside and be easily accessed.

How agentic AI and intelligent ITSM are redefining IT operations management
Agentic AI marks the next major evolution in enterprise automation, moving beyond systems that merely respond to commands toward AI that can perceive, reason, act and improve autonomously.

What is an enterprise search engine? A guide to AI-powered information access
An enterprise search engine is a specialized software that enables users to securely search and retrieve information from across an organization’s internal data sources and systems.

A comprehensive guide to AgentOps: Scope, core practices, key challenges, trends, and ZBrain implementation
AgentOps (agent operations) is the emerging discipline that defines how organizations build, observe and manage the lifecycle of autonomous AI agents.

Adaptive RAG in ZBrain: Architecting intelligent, context-aware retrieval for agentic AI
Adaptive Retrieval-Augmented Generation refers to a class of techniques and systems that dynamically decide whether or not to retrieve external information for a given query.
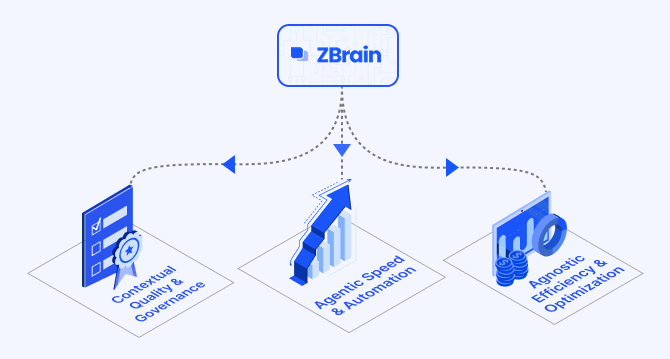
How ZBrain breaks the trade-offs in the AI iron triangle
ZBrain’s architecture directly challenges the conventional AI trade-off model—the notion that enhancing one aspect inevitably compromises another.
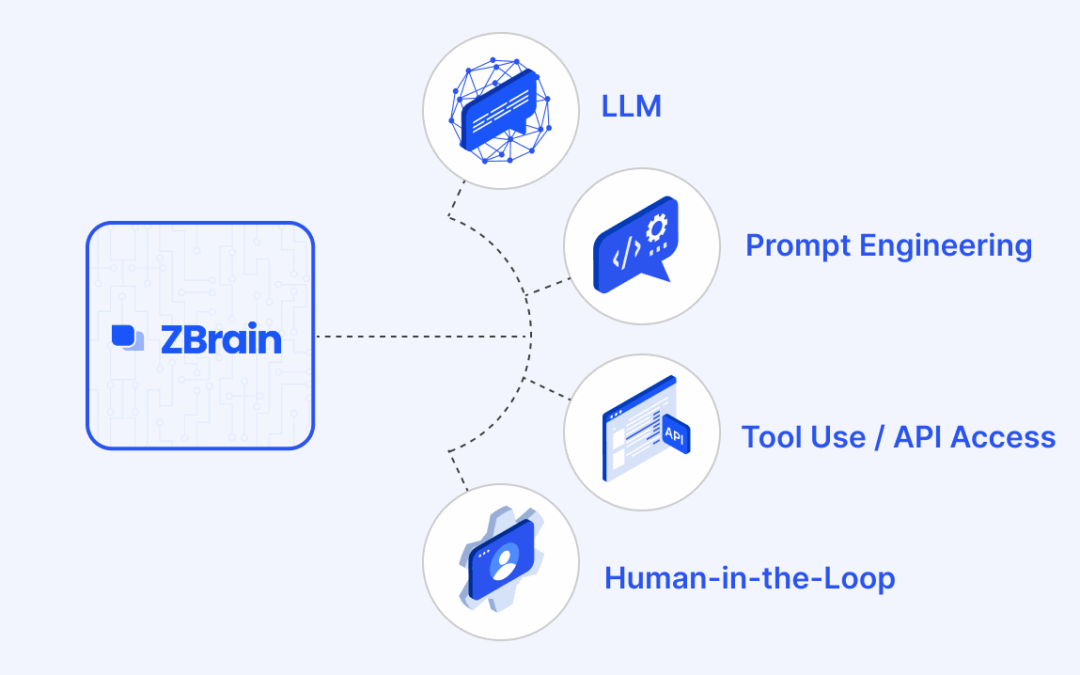
ZBrain Builder’s AI adaptive stack: Built to evolve intelligent systems with accuracy and scale
ZBrain Builder’s AI adaptive stack provides the foundation for a modular, intelligent infrastructure that empowers enterprises to evolve, integrate, and scale AI with confidence.
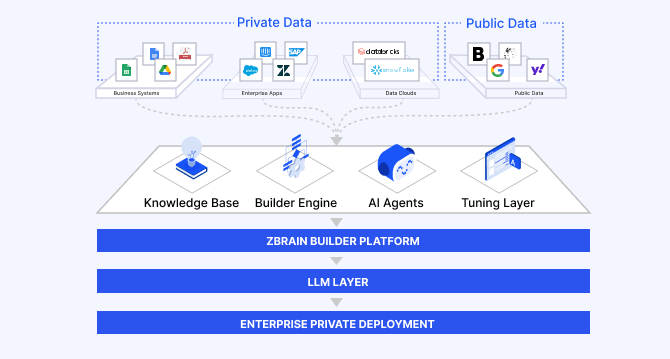
Automated AI workflows with ZBrain: Flows, LLM agents and orchestration patterns
ZBrain enables enterprises to design workflows that are intuitive for teams, efficient in execution, and adaptable to evolving business needs—transforming automation into a strategic advantage.




